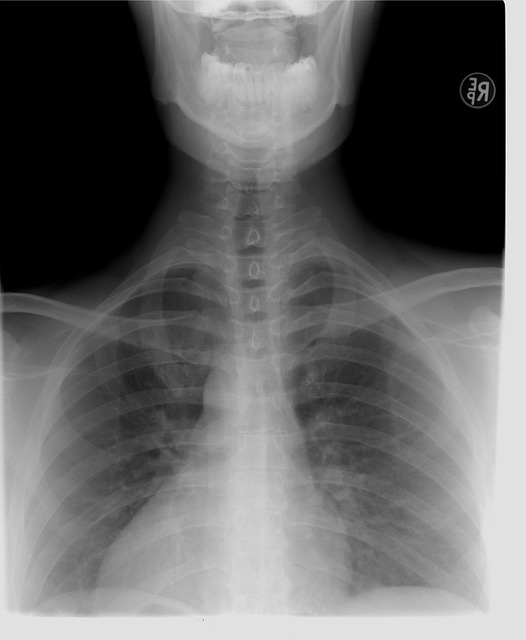
Advanced imaging techniques, notably high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT), play a pivotal role in diagnosing rib fractures and chest trauma, especially in patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD). HRCT offers detailed visualizations of costochondral junctions and muscles, enabling the detection of subtle nondisplaced rib fractures missed on standard X-rays. This advanced approach is crucial for accurate ILD diagnosis, proper management, and improved patient outcomes.
Diagnosing rib fractures and chest trauma accurately is crucial for effective patient care. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of identifying these injuries using various imaging techniques. From understanding the mechanics of rib fractures and their associated chest trauma to delving into advanced imaging technologies, we provide insights on enhancing diagnostic capabilities. Specifically, we highlight the role of interstitial lung disease imaging in traumatic contexts, offering a deeper look at this critical aspect for healthcare professionals.
Understanding Rib Fractures and Chest Trauma
Rib fractures and chest trauma are common injuries often resulting from high-impact incidents like motor vehicle accidents or falls. Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and management. These types of injuries can lead to significant pain, respiratory complications, and even life-threatening conditions if left undiagnosed or improperly managed.
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) imaging plays a critical role in diagnosing rib fractures and chest trauma, providing detailed insights into the extent of damage. Advanced imaging techniques, such as high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT), are particularly useful for identifying subtle changes in lung structure, including interstitial inflammation or fibrosis associated with ILD. This comprehensive approach ensures accurate diagnosis, enabling healthcare professionals to deliver tailored care and improve patient outcomes.
Imaging Techniques for Accurate Diagnosis
Imaging plays a pivotal role in accurately diagnosing rib fractures and chest trauma, providing critical insights that aid in patient management. Techniques like X-rays, CT scans, and MRI are instrumental in detecting and characterizing these injuries. In cases where interstitial lung disease (ILD) is suspected or co-exists with traumatic injuries, advanced imaging becomes even more crucial. High-resolution CT (HRCT) is particularly effective for evaluating ILD and identifying patterns distinct from those seen in acute chest trauma, ensuring precise diagnoses and tailored treatment plans.
For rib fractures, while initial X-rays may reveal linear fractures, HRCT can offer detailed visualizations of the costochondral junctions and intercostal muscles, helping to identify subtle nondisplaced fractures that might be missed on standard radiographs. This comprehensive approach is essential for accurate diagnosis and patient outcomes in the presence of co-morbidities like ILD or other chest pathologies.
Interstitial Lung Disease in Traumatic Contexts
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) can be exacerbated or even triggered by traumatic events, particularly chest trauma. In the context of rib fractures, which are common in accidents and falls, imaging plays a crucial role in diagnosing both the rib injuries and any associated ILD. High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is often used to assess interstitial lung disease as it provides detailed views of the lungs’ fine structures, enabling radiologists to identify patterns indicative of ILD.
The presence of chest trauma can mask or complicate the symptoms of ILD, making accurate diagnosis challenging. Interstitial lung disease imaging in traumatic contexts requires careful interpretation to distinguish between inflammation caused by the injury and pre-existing or developing ILD. Advanced imaging techniques help in identifying specific features such as honeycombing, traction bronchiectasis, and ground glass opacities, which are key indicators of ILD, ensuring proper management and treatment for both rib fractures and associated lung conditions.
Advanced Imaging Technologies and Their Role
Advanced imaging technologies have revolutionized the diagnosis of rib fractures and chest trauma, providing more detailed insights than traditional methods. High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is particularly valuable for detecting subtle fractures and evaluating interstitial lung disease imaging, as it offers superior contrast resolution compared to plain radiographs. These advanced scanners can capture intricate anatomical structures, enabling precise identification of nondisplaced or minimally displaced rib fractures that might be missed on standard imaging.
Moreover, modern imaging techniques allow for comprehensive assessment of chest trauma, including internal organ injuries and pulmonary complications. For instance, computed tomography angiography (CTA) is crucial in identifying vascular injuries and bleeding, while magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provides valuable information about soft tissue damage and neural integrity. Integrating these advanced imaging tools into clinical practice has significantly improved diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes in cases of rib fractures and chest trauma.
In conclusion, accurate diagnosis of rib fractures and chest trauma is paramount for effective patient management. Through a comprehensive understanding of these conditions, along with the application of advanced imaging techniques like CT scans, X-rays, and emerging technologies, healthcare professionals can reliably detect even subtle abnormalities, including interstitial lung disease caused by traumatic events. This ensures prompt treatment and improved outcomes for patients suffering from chest trauma.